
Unlocking Emotional Resilience: A Guide to the Safe and Sound Protocol (SSP)
Unlocking Emotional Resilience: A Guide to the Safe and Sound Protocol (SSP) In today’s world, managing stress, building emotional resilience,
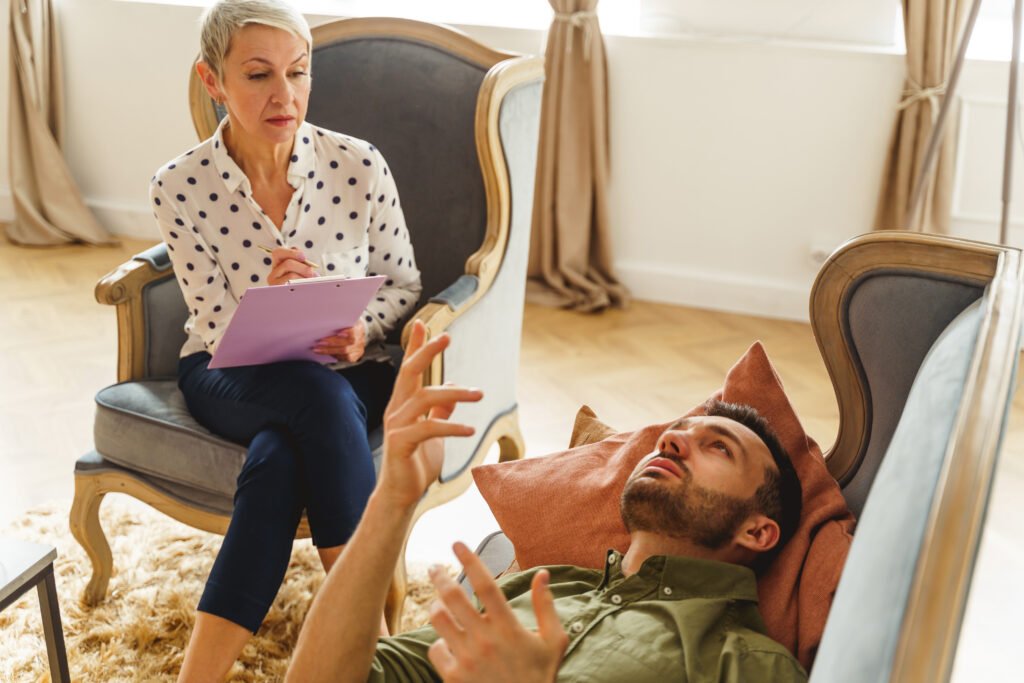

Psychotherapy and the Brain
While psychotherapy is primarily focused on addressing mental and emotional concerns, its impact extends far beyond the mind. Recent research has shed light on the profound neurological changes that can occur as a result of psychotherapy.
Neuroplasticity and Neural Pathways
One of the key ways psychotherapy changes the brain is by promoting neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and create new neural connections. Through techniques like cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), individuals can learn to restructure their thought patterns and behaviors, which can lead to physical changes in the brain’s neural pathways.
Neurotransmitter Regulation
Additionally, psychotherapy has been found to influence the levels of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which play crucial roles in mood regulation and reward processing. By addressing imbalances in these neurotransmitters, psychotherapy can alleviate symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
Lasting Neurological Impact
The neurological changes induced by psychotherapy are not merely temporary; researchers have observed that these changes can persist long after the therapy has concluded. This highlights the potential for psychotherapy to have a lasting impact on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being, as well as their overall brain function.
Conclusion
The field of neuroscience has provided valuable insights into the profound impact of psychotherapy on the brain. By promoting neuroplasticity, regulating neurotransmitter levels, and inducing lasting neurological changes, psychotherapy offers a powerful tool for addressing mental health concerns, fostering personal growth, and enhancing overall well-being.

Unlocking Emotional Resilience: A Guide to the Safe and Sound Protocol (SSP) In today’s world, managing stress, building emotional resilience,

What is Mindfulness Therapy? Mindfulness therapy refers to a range of therapeutic approaches that utilize mindfulness practices and principles to
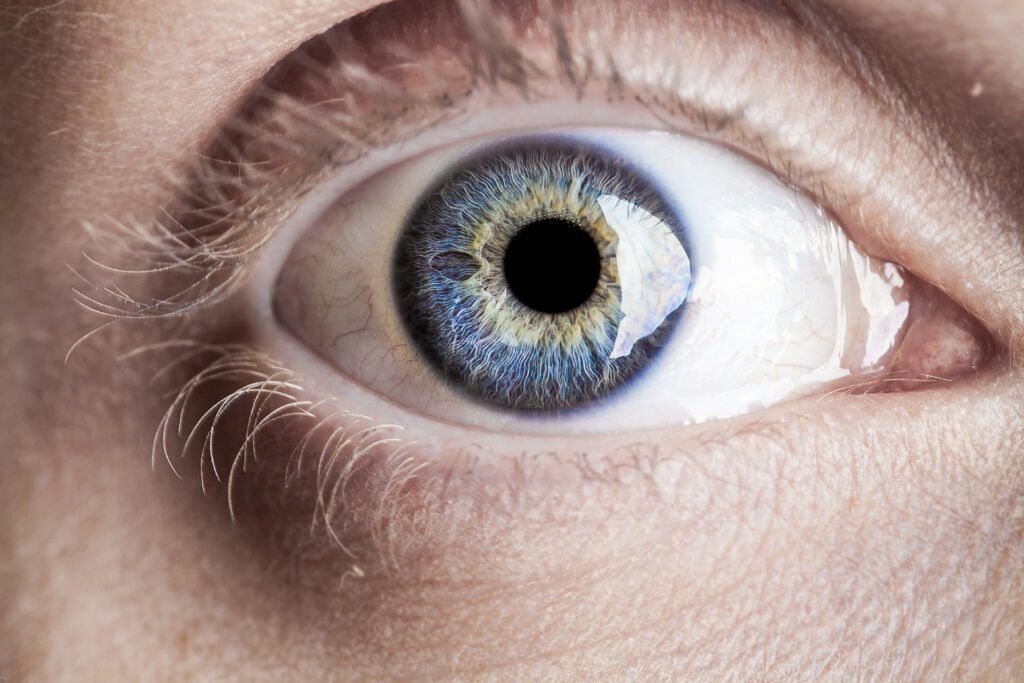
What is EMDR? EMDR stands for Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing. It is a form of psychotherapy that was originally
Whether you're navigating trauma, seeking personal growth, or looking for short-term, focused therapy, I am here to support you. If you're ready to start your journey toward greater self-understanding and emotional well-being, I invite you to reach out.
SW6, SW7, SW2, W8, SW3, SW11, SW17, SW18, SW15, SE1, SE2, NW1, W11, NW2, TW9, TW10, WC1
Bilo da prolaziš kroz traumu, tražiš lični rast ili si u potrazi za kratkoročnom, usmerenijom terapijom, tu sam da ti pružim podršku. Ako si spremna da započneš svoje putovanje ka većem samorazumevanju i emotivnom blagostanju, pozivam te da mi se javiš.
@2024 Dee Marsenic Psychotherapy Practice